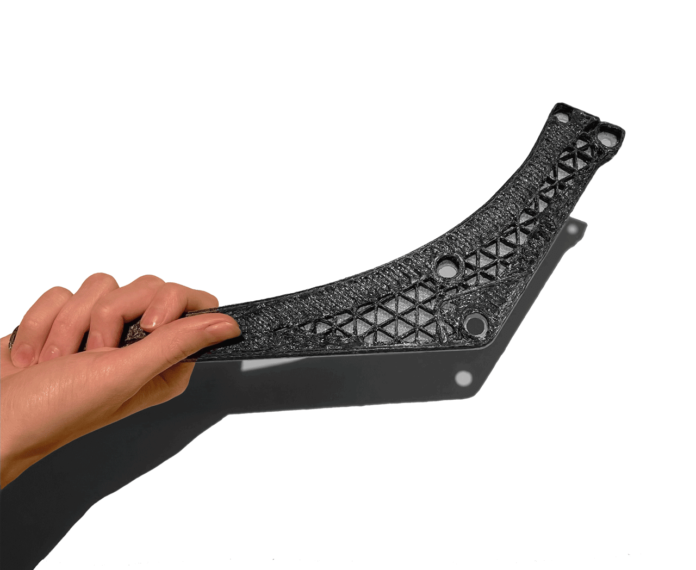
The collaboration that is sparking our interest today is a “3D printer+ software” one. For composite 3D printing, Anisoprint and Additive Flow have decided to join forces to improve composite materials design.
As you know, Anisoprint is one of the 3D printing startups that are investing extra miles to advance composite 3D printing through 3D printers, materials and software. As a matter of fact, today, the Luxembourg company has decided to enhance the use of its slicing software by enabling compatibility with a full-scale CAE tool.
To do so, the team relied on Additive Flow’s expertise in AI-powered multimaterial optimization. With this compatibility between Aura and the full-scale CAE tool, it becomes possible to optimize geometry smoothly through all phases of the design process.
“Design for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM) is one of the hottest topics. Not only because different additive manufacturing technologies require a specific approach for design, but they make designs that were impossible before possible now. As technology developers, we need to offer our customers tools and a smooth workflow for DfAM, that will help to get the most out of the unique hardware and material capabilities our solutions provide,” said Fedor Antonov, CEO of Anisoprint. “We are happy to find partners with whom we can shortcut the long and difficult R&D cycle of developing a DfAM solution, fully capable to support Anisoprinting. And it is already available for users within a simple workflow and native integration of our software products – Formflow and Aura 2.4.”
Why it is pivotal to optimize composite materials
Experience in composites reveals a number of advantages in R&D & production applications. However, the Holy Grail of achieving these applications remains costs.
According to the Anisoprint team, versatility of composites can help overcome this challenge. They explain for instance, that composite fiber, being an anisotropic material, exhibits different properties in different directions. Effectively using these characteristics can result in a 20-fold increase in mechanical parameters, such as stiffness.
On the other hand, at the very beginning, it’s crucial to know how to design anisotropic structures, specifically for fiber paths, load simulation patterns, calculating thermal exposure, weight, and many other tasks. Well, imagine now if you don’t have any expert in structural performance of materials?
To avoid slowing down the production process with these materials, Additive Flow addresses this challenge with their software Formflow – a specific CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) tool for performance analysis and structural anisotropic design that will result in the most effective topology for given parameters.
This new feature will enable automation and accuracy in the development of designs with anisotropic structures. Additive Flow also explains that the trial and error method will now be replaced by physics simulating algorithms that define optimally performing parts. Operators could also appreciate costs savings through integration of topology, enhanced flexibility due to clear quantitative analysis of loads as well as the optimized material use. The latter advantage means that parts designed with minimal weight and maximal desired parameters lead to reasonable and efficient material consumption.
Testing for optimization of internal structure of a continuous fiber reinforced part
The image bellows show an aircraft chair support layer by layer designed to be light weight and withstand sufficient loads.
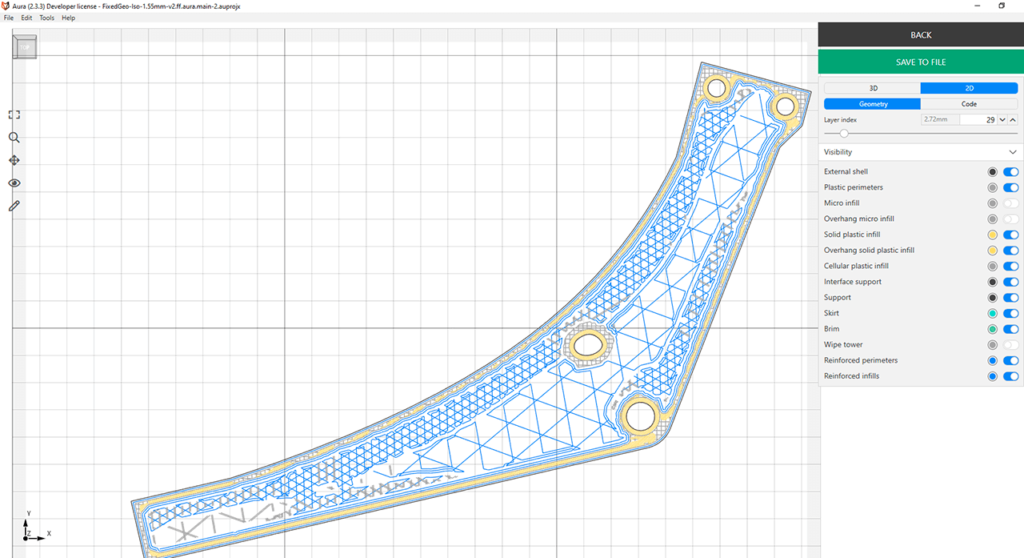
“The darker areas indicate a more dense lattice that reinforces the most loaded regions.
Naturally, the more dispersed grid here fills the areas that carry less load: thus we do not waste material by over-reinforcing them. Using the optimal amount of material leads to reducing printing time, less material waste and reduced costs.
It is peculiar how a simplistic detail starts to resemble natural structures once we see how boundary conditions really work. The sophisticated pattern of lattices (they function as multimaterial here) gives an exhaustive reason why we need reliable software for composite materials design to make the most of continuous fiber 3D printing.”
“Our accessible UI provides an integrated workflow to exploit material property <> parameter relationships, and allow these to be efficiently applied through repeatable workflows. Results selection is made simple with visualization comparison tools – and streamlined export with build-file formats, including Aura,” said Alexander Pluke, Additive Flow CEO. “We’re excited to be working with Anisoprint and their enhanced multi-property capability that can deposit different materials, and tune anisotropic properties to meet specific strengths and engineering requirements.”
Anisoprint has recently took part in a dossier dedicated to “composite 3D printing, understanding the value proposition of a niche technology.”
Additive Flow has recently took part in an Additive Talks session dedicated to the optimization of multi-functional parts.
Remember, you can post job opportunities in the AM Industry on 3D ADEPT Media free of charge or look for a job via our job board. Make sure to follow us on our social networks and subscribe to our weekly newsletter : Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn & Instagram ! If you want to be featured in the next issue of our digital magazine or if you hear a story that needs to be heard, make sure you send it to contact@3dadept.com






