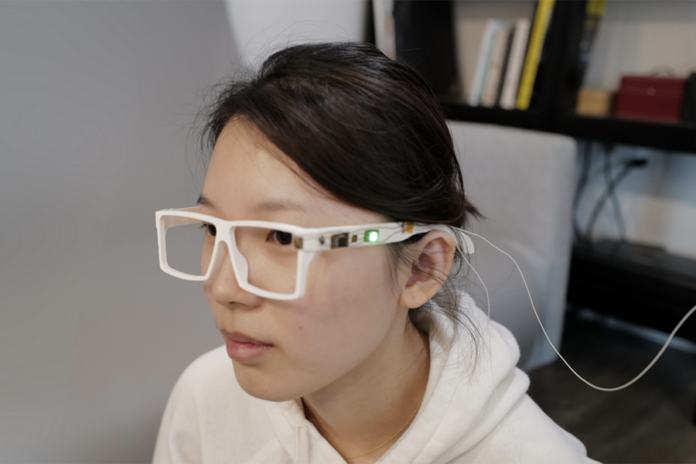
Despite the advancements of 3D printing, it remains a challenge to manufacture electronic components. The manufacturing of parts that would embed sensors, chips, and tags for instance, requires the engineer to design parts separately, making it difficult to create items where the added functions are easily integrated with the form.
To address this issue, MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) has imagined a 3D design environment named MorphSensor. The latter would let users iterate an object’s shape and electronic function in one cohesive space, to add existing sensors to early-stage prototypes.
“MorphSensor fits into my long-term vision of something called ‘rapid function prototyping’, with the objective to create interactive objects where the functions are directly integrated with the form and fabricated in one go, even for non-expert users,” says CSAIL PhD student Junyi Zhu, lead author on a new paper about the project. “This offers the promise that, when prototyping, the object form could follow its designated function, and the function could adapt to its physical form.”
MorphSensor in action
Imagine being able to have your own design lab where, instead of needing to buy new items, you could cost-effectively update your own items using a single system for both design and hardware.
For example, let’s say you want to update your face mask to monitor surrounding air quality. Using MorphSensor, users would first design or import the 3D face mask model and sensor modules from either MorphSensor’s database or online open-sourced files. The system would then generate a 3D model with individual electronic components (with airwires connected between them) and color-coding to highlight the active sensing components.
Designers can then drag and drop the electronic components directly onto the face mask, and rotate them based on design needs. As a final step, users draw physical wires onto the design where they want them to appear, using the system’s guidance to connect the circuit.
Once satisfied with the design, the “morphed sensor” can be rapidly fabricated using an inkjet printer and conductive tape, so it can be adhered to the object. Users can also outsource the design to a professional fabrication house.
To test their system, the team iterated on EarPods for sleep tracking, which only took 45 minutes to design and fabricate. They also updated a “weather-aware” ring to provide weather advice, by integrating a temperature sensor with the ring geometry. In addition, they manipulated an N95 mask to monitor its substrate contamination, enabling it to alert its user when the mask needs to be replaced.
In its current form, MorphSensor helps designers maintain connectivity of the circuit at all times, by highlighting which components contribute to the actual sensing. However, the team notes it would be beneficial to expand this set of support tools even further, where future versions could potentially merge electrical logic of multiple sensor modules together to eliminate redundant components and circuits and save space (or preserve the object form).
Zhu wrote the paper alongside MIT graduate student Yunyi Zhu; undergraduates Jiaming Cui, Leon Cheng, Jackson Snowden, and Mark Chounlakone; postdoc Michael Wessely; and Professor Stefanie Mueller. The team will virtually present their paper at the ACM User Interface Software and Technology Symposium.
Remember, you can post free of charge job opportunities in the AM Industry on 3D ADEPT Media or look for a job via our job board. Make sure to follow us on our social networks and subscribe to our weekly newsletter : Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn & Instagram ! If you want to be featured in the next issue of our digital magazine or if you hear a story that needs to be heard, make sure to send it to contact@3dadept.com