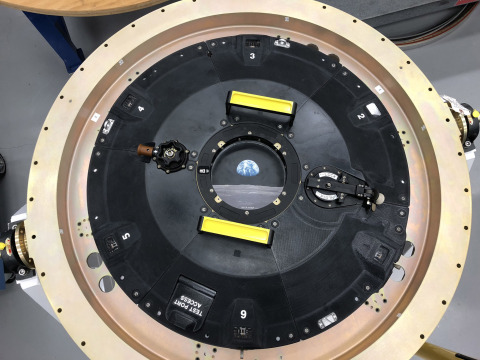
Two days ago, we were talking about the new material of Stratasys: Antero 800NA used to additively manufacture parts exposed to chemicals and high temperatures. Today, the Orion spacecraft exploits the potential of this material to fabricate a connected 3D printed docking hatch door.
Phoenix Analysis & Design Technologies, Inc. (aka PADT) and Lockheed Martin Space will collaborate on this project together. In addition to this recently unveiled material of Stratasys, both companies will use an ESD variant of the new Antero™ 800NA.
A few words on Orion’s mission
Orion is NASA’s spacecraft that will send astronauts to the Moon and beyond. Orion’s next test flight, dubbed Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), will be the first integration mission with the rocket Space Launch System, where an un-crewed Orion will fly thousands of miles beyond the Moon during three weeks.

However, as part of the EM-2, astronauts will use over 100 3D printed production parts on board manufactured by Stratasys, Lockheed Martin and PADT.

As far as the manufacturing is concerned, the team will use materials such as ULTEM 9085™ resin and the new Antero material incorporating critical electro-static dissipative (ESD) functionality. Since we are talking about manufacturing parts in/for the space, it should be noted that these materials should be highly resistant and capable to resist under high temperatures. We already know that the new Antero 800NA is used with the FDM technology.
Further information will be given at the end of the mission. For now, let’s hope everything goes well for the preparation of the EM-2.
For further information about 3D Printing, follow us on our social networks and subscribe to our newsletter!
Would you like to be featured in the next issue of our digital magazine? Send us an email at contact@3dadept.com





