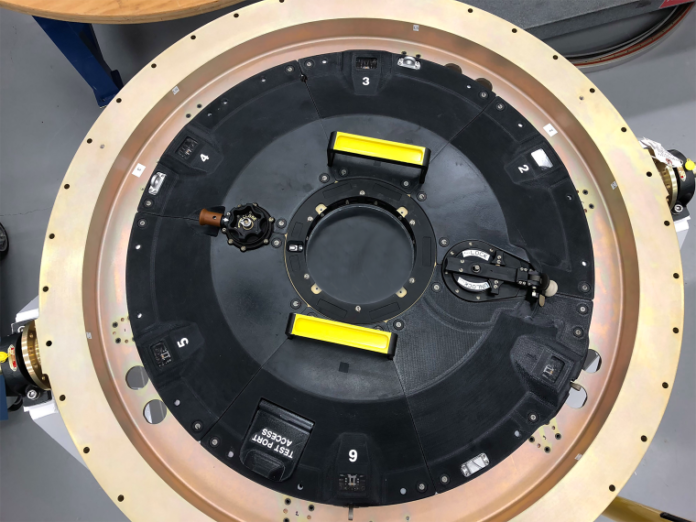
AM company Stratasys, aerospace company Lockheed Martin and Metropolitan State University of Denver provide the public with baseline material qualification data for Antero 840CN03 filament material.
As a reminder, this material is leveraged to produce 3D printed parts for NASA’s Orion Mission. The release of this qualification data allows those in the industry to use the material for additively manufactured aerospace parts.
“We want to demonstrate a new model for how industry, manufacturers and academia can collaborate to gather and release material qualification data that helps accelerate the adoption of additive manufacturing across the aerospace industry,” said Foster Ferguson, Director of Aerospace for Stratasys.
Designed for space-ready performance, Antero 840CN03 is a blended and functionalized PEKK-based high-performance, ESD thermoplastic composite material developed specifically for production-grade Stratasys FDM® 3D printers that meets ESD performance and NASA outgassing requirements while also exceeding the flame, smoke, and toxicity (FST) characteristics required for aviation applications.
During this first phase of qualification, a baseline set of data was collected by printing over 280 test coupons in Antero 840CN03 on Stratasys Fortus® F900® 3D printers at Lockheed Martin in Littleton, Colo., and Stratasys Direct Manufacturing in Belton, Texas. Coupons were tested for tensile strength properties which is a key mechanical property for design. Data collected confirmed the high performance of the Antero material as well as the consistent mechanical properties which have been previously shown in academic studies. Future phases of testing will expand to additional relevant properties, giving design engineers additional data to work with in applying Antero to other part types and environments.
“We are continually looking for ways to drive innovation for flight-qualified materials and additive manufacturing is key to that endeavor,” said Cris Robertson, Associate Manager of Advanced Manufacturing at Lockheed Martin Space. “Through our collaboration with Stratasys and MSU Denver, we have collected the data necessary to qualify Antero 840CN03 for flight parts and we are now able to expand our use of the material beyond our initial applications on the Orion vehicle.”
MSU Denver is educating and training the manufacturing workforce of the future using additive and subtractive manufacturing that can reduce costs and increase application capabilities.
“These types of research and development collaborations with leading companies like Stratasys and Lockheed Martin enable our students to be well prepared to help their future aerospace employers with adopting the latest technology in the industry,” said Mark Yoss, Director of the Advanced Manufacturing Sciences Institute at MSU Denver. “By publishing this material qualification data, we can help move the aerospace industry forward by establishing more standards in additive manufacturing.”
Remember, you can post job opportunities in the AM Industry on 3D ADEPT Media free of charge or look for a job via our job board. Make sure to follow us on our social networks and subscribe to our weekly newsletter: Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn & Instagram ! If you want to be featured in the next issue of our digital magazine or if you hear a story that needs to be heard, make sure you send it to contact@3dadept.com